Protective Call
All Option Strategies
Protective Call is a hedging options strategy used for minimising risks.
It combines an existing short position on an underlying asset with buying of call options, to safeguard against the price rise against the expectations. Premium needs to be paid for buying the call option, however, the risk of price movement gets minimised.
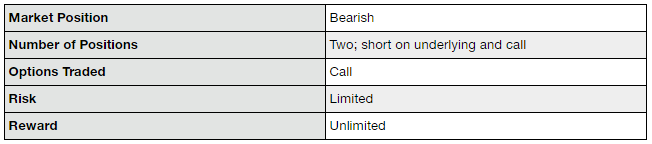
The protective call strategy is used when the trader is bearish towards the market and is expecting the prices to go down.
Therefore, he holds a short position on the underlying asset. However, in order to make sure that he does not suffer huge losses if the price of the underlying goes up instead, he also buys the call options on the same underlying asset.
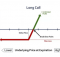
Thus, the protective call is a protection against the price reversal and works like an insurance policy. The profits expected can be retained and the losses can be averted with the right use of a protective call.
The protective call is also called the synthetic long put because its risk and reward profile is similar to a long put.
The maximum profit is unlimited. The profits will keep on increasing as the price of the underlying asset keeps on going down.
The maximum risk is limited to the amount of the premium paid to buy the call option.
Thus, the protective call is a simple and widely used hedging strategy used by the investors to protect their profits earned, while still keeping the positions open. It is incorporated by short sellers to limit their upside risk.
Protective Call Strategy Timing
The protective call strategy comes into play when the investor is bearish towards the market and is expecting the market to go down.
At the same time, the investor is uncertain that the prices may go up. In such a situation, the cautious bear will buy a protective call to protect against the upward rise in prices and retain his profits, in event of an upturn by the stock.
The protective call strategy is rightly used only at times of uncertainty.
If the investor is sure of the bearish trend, he must only keep his short positions open and not add the expense of buying the call option. The premium paid for the call option will reduce his profit by some amount.
At the same time, when the investor is certainly bullish towards the trend, he should rather simply sell the stock and prevent any losses. The premium paid for call option will only end up adding to his losses.
The benefit of using a protective call is the unlimited profit potential.
The maximum profit from the strategy is equal to the difference between the sale price of the underlying asset and the current price of the underlying, minus the premium paid for the call option. As the price of the underlying keeps going down, the profit earned keeps on going up.
At the same time, the risk from the strategy is limited.
If the price of the underlying goes up, against the expectation of the bearish investor, the call option will get exercised and the only loss that the investor will make is equal to the amount of the premium paid for buying the call option.
Protective Call Example
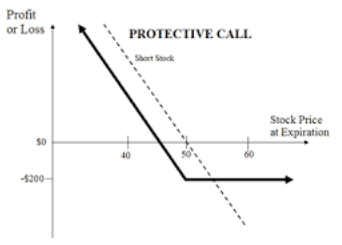
To understand the protective call strategy, we consider that a trader is selling 250 shares of Reliance Industries Limited, which are currently at a market price of ₹745 each.
To create a protective call, the trader also buys an at-the-money call option at ₹740 on the same shares at a premium of ₹22.
The lot size is 250 shares.
Scenario 1:
At the time of options expiration, if the price of the Reliance shares falls down to ₹720, as expected by the trader, he will make a profit of (745-720)= ₹25.
After paying the premium for the call option, the net profit will be (25-22) = ₹3*250= ₹750.
If the trader had not used the protective call, he would have earned the straight profit of (745-720)= ₹25*250= ₹6,250.
Thus, by paying the premium on the call option, the profit has considerably reduced. So, if the trader is certain of the bearish movement of the market, he should rather just short the shares and not use the call option.
Scenario 2:
If the price of the Reliance shares goes up to ₹760, against the bearish expectations, the short position will cause loss of (745-760)= 15*250= ₹3,750.
The call option will be exercised in-the-money and will bring in a profit of (760-740)= 20*250= ₹5,000. The net premium paid will be 22*250= ₹5,500.
The net payoff from the strategy will be -3750+5000-5500= loss of ₹4,250. This is the maximum loss from the strategy.
Thus, by using the protective call, the investor becomes able to protect himself from further losses if the price of the underlying goes up, instead of going down. The loss gets limited to the amount of premium paid and the profit still remains unlimited.
Protective Call Advantages
Here are some of the advantages of using the protective call as your options trading strategy:
- The strategy has the potential for unlimited profit.
- The risk gets limited if the market moves in the opposite direction as expected.
Protective Call Disadvantages
At the same time, there are few issues with this options strategy you must know of:
- If the prices do go down as expected, the profit will get reduced by the amount of premium paid.
Conclusion
As a bottom line, the protective call is a simple and very efficient strategy at times of uncertainty.
It helps to lock in the profits gained by shorting of the shares and protects from losses in the event that the stock prices rise up. However, a premium needs to be paid for buying the call option, which may reduce the profits.
Therefore, it is a strategy that needs the trader to understand the direction and trend of the market well. If the trend is not understood well, the profits may get diluted, without having to.
In case you are looking to invest in options or share market in general, let us assist you ahead.
More on Share Market Education: