Stock Market Crash 2008
More On Share Market
The stock market crash 2008 was one of the biggest drops since today. The chain reaction of events that took place during the period wiped off the retirement savings of most Americans and affected the economy adversely.
The major crash occurred due to the major fall of Dow Jones to 777.8 in single-day trading and the rejection of bank bail-out bill by the Congress. But the signs were visible from the time before the crash hit the market.
As compared to the stock market crash 1929 and Black Monday 1987 this stock market crash India was the worst in which the Dow falls to its maximum value.
Also Read: Sectors in Stock Market India
The financial chaos raised due to stock market crash 2008 led to
- Massive job loss
- Mortgage defaults
- Downfall of investment firms
- Bankruptcy of many automakers
In all, the crisis of the stock market pushed the World Bank towards the edge of collapse.
But the major question is how the stock market crash 2008 took place? Here are the facts, causes and the major effects of the biggest stock market crash.
Also Read: Stock Market Movies
Read the information below and learn how to keep the savings and securities safe if such a crisis occurs again.
Stock Market Crash 2008 Timeline
The stock market crash of 2008 did not take place all of a sudden. In fact, the series of events and the warning signs were visible from the year ahead, the crash occurs due to the ignorance of such signs.
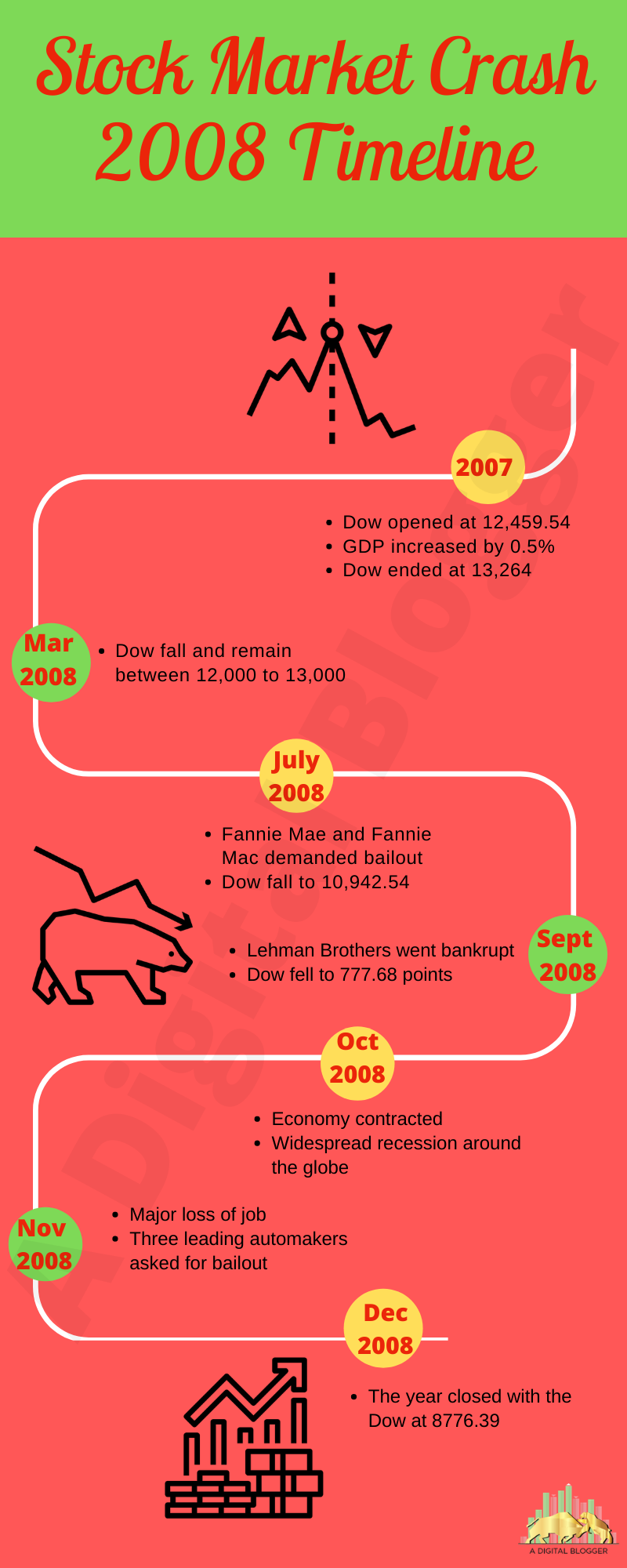
2007
Dow opened at 12,459.54 even after the raising concern about the subprime mortgage crisis (the occurrence of crisis when the bank sold too many mortgages to meet the demand of mortgage-based securities that are sold through the secondary market).
By the third quarter of the year, Gross Domestic Product increased by 0.5%. Also, the Bureau of Economic Analysis found the growth estimate to be higher and the end of the year Dow ended at 13,264 which is almost equal to the value in October 2007
March 2008
As per the study in 2007 by the BEA, the GDP growth estimation reveals that there was only 0.6% growth in the fourth quarter of 2007 with the loss of 17,000 jobs since 2004.
Dow falls and remained between 12,000 to 13,000 till March 2008.
On March 17, the Federal Reserve became active and works towards protecting the financial bank and firms like Bear Stearns who were failing at the time.
The Dow dropped to 11,650.44 but soon recovered and by May the value rose to 13,000.
July 2008
In July 2008, the two government-sponsored agencies namely; Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac were affected by the crisis and demanded the market bailout.
To help these agencies, the Treasury-Department paid the amount of $25 billion of their loan and purchased the shares of their stock while the Federal Authority offered the financial help of $300 billion.
Due to the prevailing conditions, the Dow fell to 10,924.54 and got stable at 11,000 for the rest of the summer.
September 2008
In September 2008, the chilling news of the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers hit the market and the day eventually closed with the drop of Dow by 504.48 points.
Continued with the same scenario, the big news swept out on September 16, 2008, that highlighted the bailed out of American International Group. By making $85 billion loans for 79.9% equity the Fed took ownership of the AIG.
With the collapse of Lehman Brothers, there was a loss of $196 billion that increased the panic among many businesses. Bank has driven up the rates as they were afraid to lend money.
By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points.
By the end of the week on September 19, 2008, the Fed established the Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility that committed to offer loans to banks to buy Commerical paper from the money market funds. The day was ended at the Dow value of 11,388.44.
On September 20, 2008, the bank bailout bill was sent to Congress by Secretary Paulson and Federal Reserve Chair. The Dow fell to 777.68 points during the intraday trading that increased panic in the Global Market.
The prevailing panic condition resulted in the following outcome:
- Drop of Brazil Ibovespa to 10%
- The drop in London FTSE to 5.3%.
- Increase of Gold to over $900 per ounce
- Drop in the oil value to $95 a barrel.
To bring back the financial stability the Fed took an initiative and doubled the currency swaps with the foreign central banks of different countries including Europe, England, and Japan.
Also Read: How To Invest In Foreign Stocks
October 2008
In October 2008 the congress passed the bailout bill.
The Dow Dropped 800 points and closed at 10,000 on October 6, 2008.
The Fed lowered the Fed Funds rates to 1% and the Libor bank rose the lending rate to 3.46%.
The Economy further contracted by the end of the month and the whole nation faced recession.
November 2008
The economy had lost 240,000 jobs in October.
AIG bailout great to $150 billion
The major automakers asked for the federal bailout.
December 2008
The Dow ended at 8776.39 which was 34% lower than that was in the beginning.
2009
The Dow rose to 9034.69 in January 2009 and by July 24, 2009, the Dow reached a higher value and closed at 9093.24 which almost ended the stock market crash 2009.
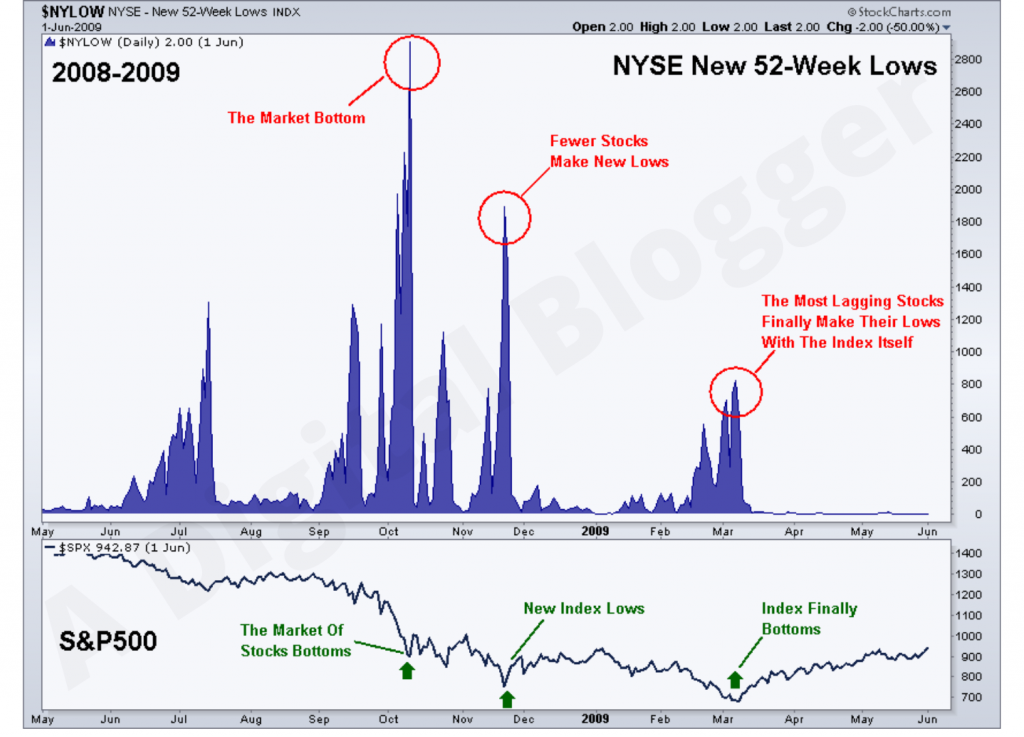
Stock Market Crash 2008 Graph
The stock market crash 2008 prevailed for long affecting the market economic condition adversely. In March 2009, the S&P500 closed to its least value. Since S&P500 is about 1 index with 500 stocks.
Since at the time, the stocks were at the bottom of the line during the first quarter of 2009.
The chart below is the list of NYSE 52-week lows during the year 2008-09. The chart depicted how the S&P500 that was on its peak in October 2008 drew to its least value in March 2009.
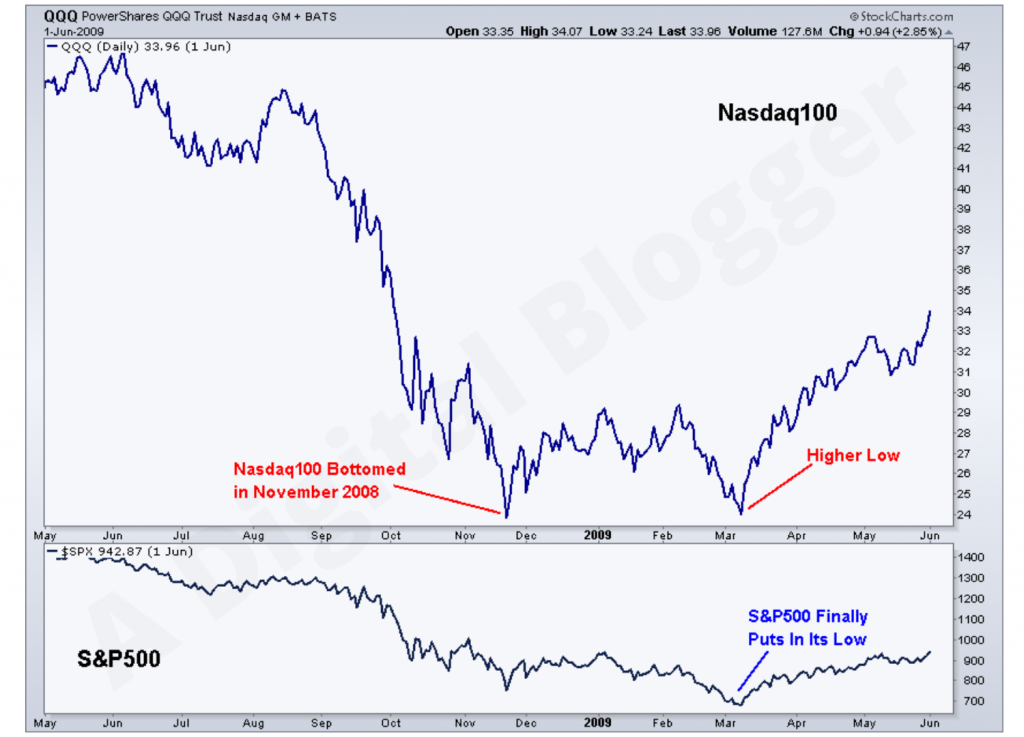
Apart from S&P500, there were other stocks as well whose value was lowered even before the former. One such example is of Nasdaq100 that was at its least value in November 2008.
To keep an eye on such a crash and to get a better insight into the market it is good to get a clear understanding of stock market charts and graphs.
Stock Market Crash 2008 Causes
Stock Market Crash 2008 was one of the greatest jolts that affected the world’s financial system the most. There is no doubt behind the saying, that the crash pushed the banking system towards the edge of collapse.
The 2008 crash took place on September 29, 2008, when the fall of Dow Jones Industrial Average to 777.68 per cent.
The crash began in the US and later spread to Europe that tended to affect many US and Europe financial firms.
On November 17, 2006, the U.S. Commerce Department presented the warning signs regarding the permit of New Home in October which was about 28% lower than the year before.
Although the warning sign was clear many economists ignored them and continued their respective activities in the market.
On September 15, 2008, when Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy the then-President George W Bush announced that there would be no bail-out.
Along with these, there were a series of events and number of causes that led to a stock market crash 2008.
The major cause of the stock market crash 2008 is found to be the explosive growth of the subprime mortgage market that began in 1999.
However the exact factor or reason for the stock market crash 2008 is still a mystery, but some general agreements define the causes of the crash.
Some of the top reasons for the crash are:
- Mild Recession in the Federal Reserve
Federal Reserve the Central Bank was facing a mild recession since 2001. The recession period resulted in the reduction of the federal funds rate from 6.5 to 1.75 from May 2000 to December 2001.
This reduction enabled the bank to extend the consumer credit at a lower prime rate and to lend to subprime or high-risk customers.
The uplift of such a scenario attracts many customers with a low credit score to borrow money for purchasing durable goods, especially house.
This increases the home rates at the accelerated speed thus causing the “housing bubble”.
- Mortgage Loans to Subprime Customers
The changing scenario of banks helped them to offer the subprime mortgage loans that are either structured with the balloon payments (due to the large payment by the end or near the end of the loan period) or with the adjustable interest rates.
The increase in the prices of homes helped the subprime borrowers to protect themselves from the high mortgage payment with different options offerings like refinancing, borrowing against the increased value of the home, selling home at good profits, etc.
In such a prevailing case, the bank can repossess the property and sell it at a higher price than the original loan.
This encouraged many banks to market subprime loans to customers having poor credit assets. They were aware that they would not be able to repay the loan and mislead them with the risks involved.
All this activity of banks resulted in an increase in the share of the subprime mortgage from 2.5% to 15% from 2004-2007.
- Widespread Practice of Securitization
In simple terms, securitization is a practice of pooling together different types of debt like mortgages and other loans of customers and selling them as bonds to investors. Such bonds that consist of mortgage known as mortgage-backed securities or MBSs.
Selling and buying subprime mortgages was considered to be a good way.
Selling subprime mortgage increased the liquidity thus reducing the exposure to risky loans while the purchasing MBSs helped banks to diversify the portfolio and to earn money.
The increasing value of the home had made MBSs popular that increased the prices in the capital market accordingly.
- Depression-Era of Glass-Steagall Act (1933) and Weakening of Net Captial Requirement
The fourth cause of the crash of 2008 was found to be the depression era Glass Steagall Act (1933) that allowed banks, securities firms and other insurance companies to enter into each other’s markets resulting in the formation of the bank that was too big to fail.
Also, the SEC in 2004, weakened the net capital requirement thus encouraging the bank to invest more money in MBSs. Although the decision took by SEC resulted in enormous profit but it also exposed the portfolio to a significant risk.
- Stability in the Economic Growth
The long-prevailing stable economic condition and Great-Moderation convinced many US executives, government officials, and economists that led to the major ignorance of the discount clear-signs of the impending crisis.
Thus, the banks and other financial institutions continued the practice of reckless lending, borrowing, and securitization.
Stock Market Crash 2008 Effects
- Unemployment Rate Peaked at 10 Percent
The debilitating economic condition led to the loss of hundreds to thousands of jobs that resulted in reaching the unemployment rate to its peak at 10 per cent.
- Verge of Bankruptcy of Biggest Automakers
The three biggest automakers namely General Motors Company, Chrysler LLC, Ford Motor were on the verge of bankruptcy.
Among these three, the two names, General Motors and Chrysler LLC were taken over by the Federal Government while the Ford Motor Company received a bailout from the Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility
- Slow-Down of Housing
Since the home prices were declining progressively, homeowners found themselves in the position of upside down in terms of mortgages.
In this scenario of job losses and increasing mortgage payments, many people lost their homes.
- Loss of Job
The year 2008-09 marked the period of the Great Recession. Around 8.7 million jobs were lost and many people experienced a sharp decline in the retirement savings that contributes to the compounded unemployment and housing instability.
- Decelerated Economic Growth
The home began to lose its value along with the declining stocks that contributed to around an average of $100,000 per US household. The slower economic growth further resulted in the U.S. economy to reach around $648 billion.
- Dow Jones Hit Bottom
The Dow Jones hit the lowest value in the first quarter of 2009. This increased the panic state and accelerate economic decline.
Conclusion
The housing market was facing slower growth in 2007 but the warning signs of the impending recession generated at the time were being ignored.
The World Bank later in Jan 2008 highlighted this slow down when the economic condition was affected due to the credit crunch.
In all, the stock market crash 2008 as a result of a series of events that eventually led to the failure of some of the largest companies in the US.
With the housing bubble burst at the same time, the banks and other financial institutions were equally affected.
The period affects every other of different age groups and even led to the loss of retirement savings funds.
Seeing such a scenario, it is very important for investors to diversify their investment and to learn how to invest in the share market without any risk.
If you are looking to know more about the Indian Share Market basics, here are some reference tutorials for you: